Configuration
EnterpriseBacula Enterprise Only
This solution is only available for Bacula Enterprise. For subscription inquiries, please reach out to sales@baculasystems.com.
Fileset Configuration
Once the plugin is successfully authorized, it is possible to define regular filesets for backup jobs in Bacula, where we need to include a line similar to the one below, in order to call the Google Workspace Plugin:
Fileset {
Name = FS_GW
Include {
Options {
signature = MD5
...
}
Plugin = "gw: <gw-parameter-1>=<gw-value-1> <gw-parameter-2>=<gw-value-2> ..."
}
}
It is strongly recommended to use only one ‘Plugin’ line in every fileset. The plugin offers the needed flexibility to combine different modules or entities to backup inside the same plugin line. Different workspaces, in case of existing, should be using different filesets and different jobs.
Below sub-sections list all the parameters you can use to control GW Plugin behavior.
In this plugin, any parameter allowing a list of values can be assigned with a list of values separated by ‘,’.
Common Parameters
These parameters are common and applicable to all the modules of the Google Workspace Plugin.
Option |
Required |
Default |
Values |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
abort_on_error |
No |
No |
No, Yes |
Yes |
If set to Yes: Abort job as soon as any error is found with any element. If set to No: Jobs can continue even if it they found a problem with some elements. They will try to backup or restore the other and only show a warning |
config_file |
No |
The path pointing to a file containing any combination of plugin parameters |
/opt/bacula/etc/gw.settings |
Allows to define a config file where configure any parameter of the plugin. Therefore you don’t need to put them directly in the Plugin line of the fileset. This is specially useful for shared data between filesets and/or sensitive data as customer_id. |
|
log |
No |
/opt/bacula/working/gw/gw-debug.log |
An existing path with enough permissions for File Daemon to create a file with the provided name |
/tmp/gw.log |
Generates additional log in addition to what is shown in job log. This parameter is included in the backend file, so, in general, by default the log is going to be stored in the working directory. |
debug |
No |
0 |
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
Debug level. Greater values generate more debug information |
Generates the working/gw/gw-debug.log* files containing debug information which is more verbose with a greater debug number |
path |
No |
/opt/bacula/working |
An existing path with enough permissions for File Daemon to create any internal plugin file |
/mnt/my-vol/ |
Uses this path to store metadata, plugin internal information and temporary files |
customer_id |
No |
String representing the customer id associated to the Google Workspace subscription |
Cbdi2930doi |
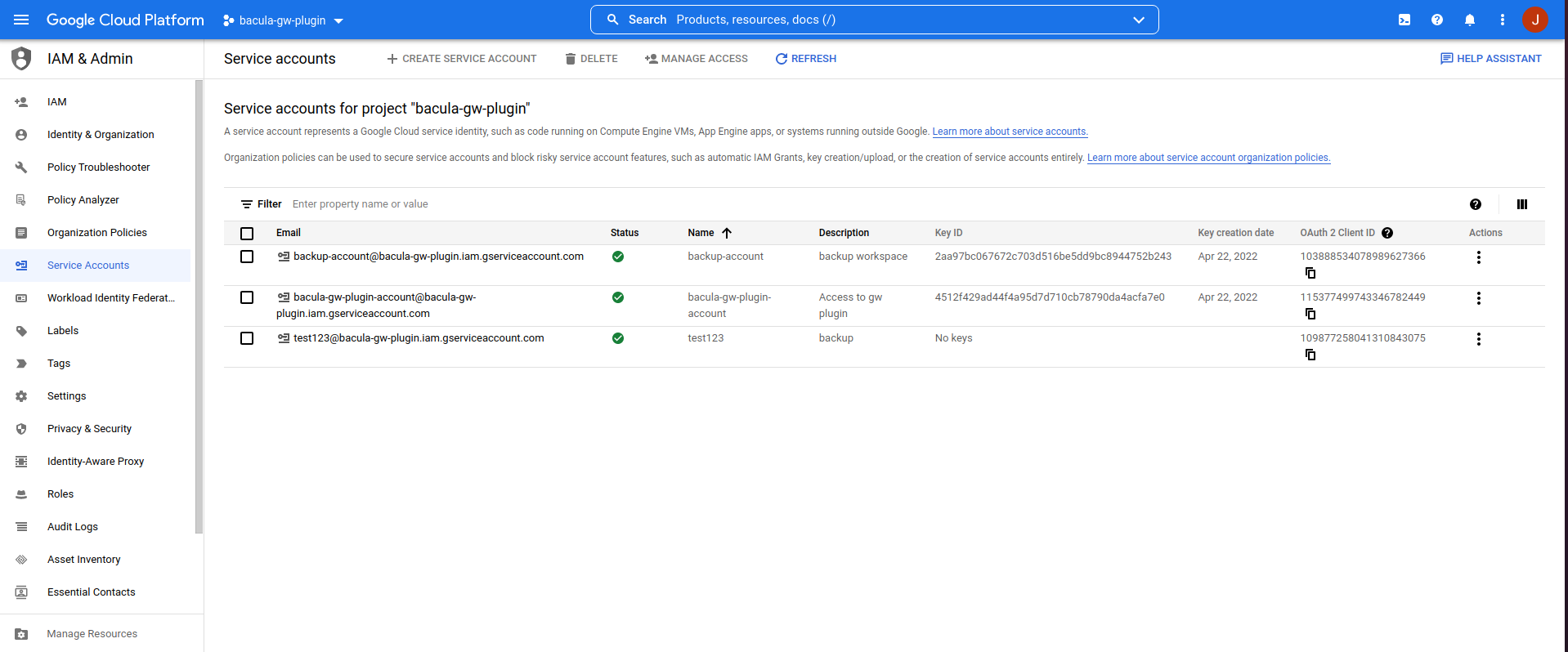
The customer id associated to the Google Workspace subscription to be backed up. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. Note that this is mandatory if you want to protect a workspace environment, but not needed to protect gmail free accounts. |
|
admin_user_email |
No |
A valid email address of one admin user of the Google Workspace subscription |
The email address of an admin user of the Google Workspace subscription to be protected. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. Note that this is mandatory if you want to protect a workspace environment, but not needed to protect gmail free accounts. |
||
credentials_file |
Yes |
The path of the file where credentials are stored |
/opt/bacula/etc/gw_credentials.json |
The path of the file downloaded from the configured Google Cloud application that will act as a bridge in order to allow the communication between this plugin and Google Workspace. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. |
|
tokens_path |
No* |
tokens |
A path with enough permissions so File Daemon can write in it |
/home/user/my_path_to_tokens |
The path that will be used to store the login cache for the device code flow authenticated users, which is relative to the path folder folder (usually working/gw/customer_id/tokens_path/). This is not used and not needed for protecting a workspace with a subscription |
auth_port |
No* |
8888 |
An integer with an open port number suitable of receiving the answer from Google Cloud services upon the delegated authentication request |
9999 |
The port to be used to open the internal service to receive the authentication answer from Google Cloud services |
service |
No |
drive, email |
drive |
Establish the service or services that will be backed up. If this is not set, the plugin will try to backup all supported services. It is recommended to split the work among different jobs when several services need to be applied. Therefore, even if this field is not required, it is strongly recommended to use it in every backup job. |
|
proxy_host |
No |
String representing DNS Name or IP address of the http(s) proxy |
myproxy.example.com |
Set up a proxy to make any plugin HTTP connection |
|
proxy_port |
No |
Integer |
3981 |
Set up the proxy port |
|
proxy_user |
No |
String of proxy user |
admin |
Set up the proxy user |
|
proxy_password |
No |
String of proxy password |
myPass123 |
Set up the proxy user password |
The plugin supports two different kind of users: Workspace users and free Gmail users.
For Workspace users, in addition to ‘credentials_file’, the following parameters are mandatory: ‘customer_id’ and ‘admin_user_email’.
For free Gmail users those parameters are not used, but it is possible to customize ‘tokens_path’ and ‘auth_port’.
Advanced Common Parameters
Following parameters are common to all Google Workspace modules (and even with some other plugins), but are advanced ones. They should not be modified in most common use cases.
Option |
Required |
Default |
Values |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
stream_sleep |
No |
1 |
Positive integer (1/10 seconds) |
5 |
Time to sleep when reading header packets from FD and not having a full header available |
stream_max_wait |
No |
120 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
360 |
Max wait time for FD to answer packet requests |
time_max_last_modify_log |
No |
86400 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
43200 |
Maximum time to wait to overwrite a debug log that was marked as being used by other process |
logging_max_file_size |
No |
50MB |
String size |
300MB |
Maximum size of a single debug log file |
logging_max_backup_index |
No |
25 |
Positive integer (number of files) |
50 |
Maximum number of log files to keep |
log_rolling_file_pattern |
No |
gw.log.%d{dd-MMM}.log.gz” |
No, Yes |
Yes |
Log patter for rotated log files |
split_config_file |
No |
= |
Character |
: |
Character to be used in config_file parameter as separator for keys and values |
opener_queue_timeout_secs |
No |
1200 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
3600 |
Timeout when internal object opener queue is full |
publisher_queue_timeout_secs |
No |
1200 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
3600 |
Timeout when internal object publisher queue is full |
The internal plugin logging framework presents some relevant features that we are going to describe:
The “.log” files are rotated automatically. Currently each file can be 50Mb at maximum and the plugin will keep 25 files.
This behavior can be changed using the internal advanced parameters: logging_max_file_size and logging_max_backup_index
The “.err” file can show contents even if no real error happened in the jobs. It can show contents too even if debug is disabled. This file is not rotated, but it is expected to be a small file in general. If you still need to rotate it, you can include it in a general rotating tool like ‘logrotate’.
Backups in parallel and also failed backups will generate several log files. For example: gw-debug-0.log, gw-debug-1.log…
Tuning Parameters
These set of parameters are common to all modules and they are advanced ones. They should not be modified in general. They can be used to tune the behavior of the plugin to be more flexible in particular bad network environments or when significant job concurrency is happening, etc.
Option |
Required |
Default |
Values |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
backup_queue_size |
No |
30 |
0-50 |
1 |
Number of maximum en-queued internal operations between service static internal threads (there are 3 communicating through queues with the set size: service fetcher, service opener and general publisher to bacula core). This could potentially affect google api concurrent requests and consequently, Google throttling. It is only needed to modify this parameter, in general, if you are going to run different jobs in parallel |
concurrent_threads |
No |
4 |
0-10 |
1 |
Number of maximum concurrent backup threads running in parallel in order to fetch or open data for running download actions. This means every service fetcher and service opener will open this number of child concurrent threads. This will affect google api concurrent requests. Google API can throttle requests depending on a variety of circumstances, but it is directly attached . It is only needed to modify this parameter, in general, if you are going to run different jobs in parallel. If you want to have a precise control of your concurrency through different jobs, please set up this value to 1. Please be careful also with the memory requirements, multi-threaded increases very significantly memory consumption per job |
api_list_page_size |
No |
500 |
1-500 |
350 |
Number of maximum elements got from Google API for each page of objects. Higher number implies less requests, but more memory and more time for each request |
api_timeout |
No |
9000 |
Positive integer (milliseconds) |
60000 |
Google call timeout inside HttpClient |
api_read_timeout |
No |
300 |
Positive integer (milliseconds) |
30000 |
Google read timeout inside HttpClient |
api_retries |
No |
5 |
Positive integer (number of retries) |
10 |
Google number of retries for retry-candidate requests |
api_retry_delay |
No |
5 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
10 |
Google API delay between retries |
general_network_retries |
No |
5 |
Positive integer (number of retries) |
10 |
Number of retries for the general external retry mechanism |
general_network_delay |
No |
50 |
Positive integer (seconds) |
100 |
General Plugin delay between retries |
stats |
No |
No |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
Yes |
Include some stats information in the joblog. Useful to measure task times |
Entity Parameters
The following list of parameters are commonly shared through any module used in the same fileset line and are intended to select the target entities to backup. Every module subsection mentions what entities are supported too.
Option |
Required |
Default |
Values |
Example |
Services |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
user |
No |
Valid email addresses of existing users on the selected workspace separated by ‘,’ |
drive, email |
Backup selected services of this list of users. If no user is provided, and no other user parameter is set, all users will be discovered and included in the backup |
||
user_exclude |
No |
Valid email addresses of existing users on the selected workspace separated by ‘,’ |
drive, email |
Exclude selected services of selected users If this is the only parameter found for selection, all elements will be included and this list will be excluded |
||
user_regex_include |
No |
Valid regex |
.*@management\.mydomain.com |
drive, email |
Backup selected services of matching users. |
|
user_regex_exclude |
No |
Valid regex |
.*@guests\.mydomain.com |
drive, email |
Exclude selected services of matching users. If this is the only parameter found for selection, all elements will be included and this list will be excluded |
|
user_suspended |
No |
No |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
Yes |
drive, email |
Includ or exclude users that have been suspended and, therefore, are not active. By default, these are excluded from any backup, as the contents cannot be regularly accessed unless the user is re-activated |
Backup Parameters
Please, check the specific module pages in order to see backup parameters that are applicable only to each of them:
Restore Parameters
The plugin is able to restore to the local file system on the server where the File Daemon is running or to the Google Workspace environment. The method is selected based on the value of the where parameter at restore time:
Empty or ‘/’ (example: where=/) → Google Workspace restore will be triggered
Any other path for where (example: where=/tmp) → Local file system restore will be triggered
When using Google Workspace restore option, the following parameters may be modified by selecting ‘Plugin Options’ during the bconsole restore session:
Option |
Required |
Default |
Values |
Example |
Services |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
destination_user |
No |
Existing email address on the target Google Workspace |
drive, email |
Destination User where restore data will be uploaded. If no user is set, every selected file will be restored in the original account |
||
destination_path |
No |
Destination path to be created (or existing) into the selected user (drive folder path) |
RestoreFolder |
drive, email |
Destination folder where all selected files to restore will be restored. If no path is set: - If no user is set either, every element will go to its original location - If a user is set using the variable destination_user: - Elements belonging to destination_user will be restored in their original location - Elements belonging to different users than destination_user will be restored in a new folder using the email address of the original user of the element |
|
send_report |
No |
0 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
1 |
drive, email |
Send a report to the user where every restore action is listed. - In drive service this will generate a new text file in the top restore folder |
allow_duplicates |
No |
1 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
0 |
drive, email |
Set if we allow to have several files with the same name in the same path or not (if not, we can overwrite the file using the ‘Replace’ general restore variable) |
drive_destination_shared_unit |
No |
Existing shared drive name |
MySharedDrive |
drive |
Destination drive shared unit where restored data will be uploaded. If no drive is set, every selected file will be restored in the original shared drive |
|
drive_skip_versions |
No |
1 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
0 |
drive |
Skip restoring former file versions (tagged with ‘###date’) even if they are selected. Important: Notice that this parameter is enabled by default, as we consider not restoring file versions the most common case. You need to disable it in order to have this kind of files restored |
drive_skip_comments |
No |
1 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
0 |
drive |
Skip restoring file comments (located inside the ‘filename_comments’ folder) even if they are selected. Important: Notice that this parameter is enabled by default, as we consider not restoring file comments the most common case. You need to disable it in order to have this kind of information restored |
drive_skip_sharedwitme |
No |
0 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
1 |
drive |
Skip restoring shared with me elements even if they are selected. |
drive_restore_share_permissions |
No |
0 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
1 |
drive |
Restore share permissions of every element in order to regenerate sharing information as allowed identities, shared links, etc. Important: Notice that this parameter is disabled by default, as we consider not restoring sharing permissions the most common case. You need to enable it in order to have shared permissions restored |
email_export |
No |
0 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
1 |
Export selected emails to MIME format in local filesystem (RFC 822) |
|
email_export_attachments_extract |
No |
1 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
0 |
Extract attachments of exported emails as independent files |
|
customer_id |
No |
String representing the customer id associated to the Google Workspace subscription |
Cbdi2930doi |
drive, email |
The customer id associated to the Google Workspace subscription to be backed up. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. Note that this is mandatory if you want to protect a workspace environment, but not needed to protect gmail free accounts. |
|
admin_user_email |
No |
A valid email address of one admin user of the Google Workspace subscription |
drive, email |
The email address of an admin user of the Google Workspace subscription to be protected. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. Note that this is mandatory if you want to protect a workspace environment, but not needed to protect gmail free accounts. |
||
credentials_file |
No |
The path of the file where credentials are stored |
/opt/bacula/etc/gw_credentials.json |
drive, email |
The path of the file downloaded from the configured Google Cloud application that will act as a bridge in order to allow the communication between this plugin and Google Workspace. Please, check the authentication section of this document for more detailed information. |
|
tokens_path |
No* |
A path with enough permissions so File Daemon can write in it |
/home/user/my_path_to_tokens |
drive, email |
The path that will be used to store the login cache for the device code flow authenticated users, which is relative to the path folder folder (usually working/gw/customer_id/tokens_path/). This is not used and not needed for protecting a workspace with a subscription |
|
auth_port |
No* |
An integer with an open port number suitable of receiving the answer from Google Cloud services upon the delegated authentication request |
9999 |
drive, email |
The port to be used to open the internal service to receive the authentication answer from Google Cloud services |
|
foreign_container_generation |
No |
1 |
0, no, No, false, FALSE, false, off ; 1, yes, Yes, TRUE, true, on |
0 |
drive, email |
Generate a general container (usually a folder) to put inside restored objects coming from different entities. For example, if we restore files from user a@workspace.com into the drive of user b@workspace.com, this option enabled will generate an automatic folder a@workspace.com inside the destination restore folder used over destination user b@workspace.com |
debug |
No |
0, 1, 2 ,3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
3 |
drive, email |
Change debug level |
See also
Previous articles:
Next articles:
Go back to: Google Workspace Plugin.