Restoring Single Database
EnterpriseBacula Enterprise Only
This solution is only available for Bacula Enterprise. For subscription inquiries, please reach out to sales@baculasystems.com.
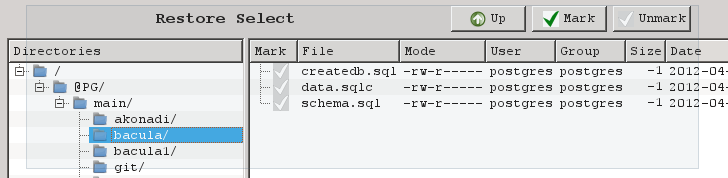
To restore a single database with the Bacula Enterprise Postgresql Plugin, the appropriate files from the database directory are selected during the restore process.
To restore the database with its original name, the selection should
only contain the data file (data.sqlc or data.sql). If the
createdb.sql file is also selected, harmless messages might be
printed during the restore.
Database Contents During Restore
To restore a single database to a new name, the two files
createdb.sql and data.sqlc (or data.sql) must be selected.
The where parameter is used to specify the new database name. If
where is set to a single word consisting of only a..z, 0-9
and _, Bacula will create the specified database and restore the
data into it.
* restore where=baculaold
...
cwd is: /
$ cd /@PG/main/bacula
cwd is: /@PG/main/bacula/
$ m data.sqlc
$ m createdb.sql
$ ls
schema.sql
*data.sqlc
*createdb.sql
If the restore process has an error such as
ERROR: database "xxx" already exists, the createdb.sql can be
skipped in the restore selection.
If the replace parameter is set to never, Bacula will check the database list, and will abort the Job if the database currently restored already exists.
Using replace=always is not recommended.
If the where parameter is a directory (containing /), Bacula
will restore all files into this directory. Doing so, it is possible to
use pg_restore directly and restore only particular contents, such
as triggers, tables, indexes, etc.
Note
Some databases such as template1, postgresql or
databases with active users can not be replaced.
See also
Previous articles:
Next articles:
Go back to: Restoring Using Dumps.