High Availability: Configuration Sync
CommunityEnterpriseIn a clustered setup, the resource manager, such as Heartbeat or Pacemaker, monitors nodes and services. When a failure occurs, it ensures that services are restarted on the appropriate node. However, it does not guarantee that Bacula’s configuration remains synchronized across cluster nodes. Ensuring consistent configuration is essential to prevent discrepancies during failover. This leads us to the question of how to synchronize the configuration across different nodes.
Synchronization Techniques
Several methods can be used to keep configuration data in sync:
Rsync: A simple and flexible approach is to run rsync at regular intervals on the active (master) node and automatically after any configuration reload.
Distributed filesystems: Provide shared, consistent access to configuration files across nodes.
External shared storage: Centralized storage accessible by all nodes, ensuring a uniform configuration.
Block-level replication: Technologies such as DRBD replicate storage blocks between nodes, offering highly reliable synchronization.
Additional details on these approaches can be found in the Architecture section of this document.
A solid and widely used option that does not rely on external elements is block-level replication using DRBD. DRBD is a mature, open-source solution that provides block-level replication for high-availability clusters. We will discuss it a bit deeper below.
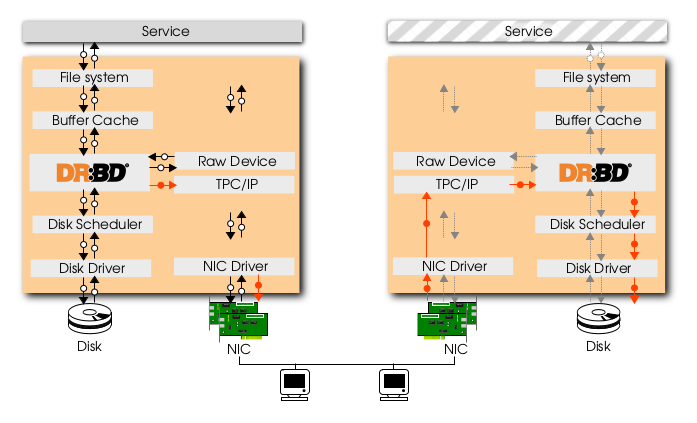
DRBD architecture
DRBD is open source and has been in development for over 20 years, with continuous improvements and new features. It is implemented as a kernel driver, several user space management applications, and some shell scripts. It is simple, fast and flexible, and uses transaction-safe technology; this means that DRBD is designed to replicate data in a reliable, secure and safe method regardless of how sensitive the data may be. DRBD is traditionally used in high availability (HA) computer clusters. Due to its focus on performance and ability to handle frequent small write operations efficiently, DRBD is often used to backup HA databases and messaging queues. It also integrates well with Heartbeat and Pacemaker.
DRBD offers support options, including installation assistance, 24/7 support, or single-incident support through LINBIT.
The performance cost of block level replication is around 10 - 15% of overall disk throughput. However, offers the significant advantage of being safe and straightforward during standby and takeover operations. It is extremely difficult to lose data due to an incorrect sequence of commands.
Streaming replication using PostgreSQL can be faster, but it requires careful steps before reactivating replication and being protected again.
Note
DRBD is also a good option for general replication needs, as mentioned in other parts of this High Availability section.
In Configuration Synchronization with DRBD: Setup, we provide an example of how to use DRBD with Bacula to replicate the configuration of a Bacula Director.
See also
Previous articles:
Next articles:
Go back to: High Availability.